Products
Dynamic Voltage Restorer
Rated Power: 3~3000KVA
Input Voltage: 380V/440V/480V±20%
Input voltage range:All(Global Power Grid)
Input frequency:40-70Hz
Output Voltage: 380V/440V/480V±1%
Output frequency:50Hz/60Hz/400Hz
Product Introduction
Voltage sag, also known as voltage drop, voltage sag, and voltage oscillation, is a type of voltage sag. It refers to the phenomenon where the effective value of voltage suddenly drops and then suddenly returns to normal. Voltage sag is the most important power quality issue in the industrial field! The factory cannot predict the occurrence of voltage sag accidents in advance!
DVR (Dynamic Voltage Restorer) is based on advanced power electronics technology, adopting a two-level topology structure, using IGBT (Infineon) as the main power device, SPWM working mode voltage and current dual closed-loop controllable voltage regulation, PID fuzzy control, ensuring stable output of voltage and frequency.When the system voltage suddenly drops, DVR can quickly adjust the voltage, eliminate the three-phase voltage imbalance, and adjust the voltage deviation to ensure seamless connection of the output voltage to the rated value, protecting the normal operation of the load.
Working principle
The DVR is connected in series between the power supply and the protected load. It continuously monitors the input side power supply voltage. Once the power supply voltage deviates from the rated voltage level, the DVR will generate a suitable compensation voltage through the IGBT inverter system to inject into the system, ensuring the output side (i.e., the load side) voltage is stable and the protected load is not affected by voltage changes.
Dynamic Voltage Restorer Control Principle Diagram
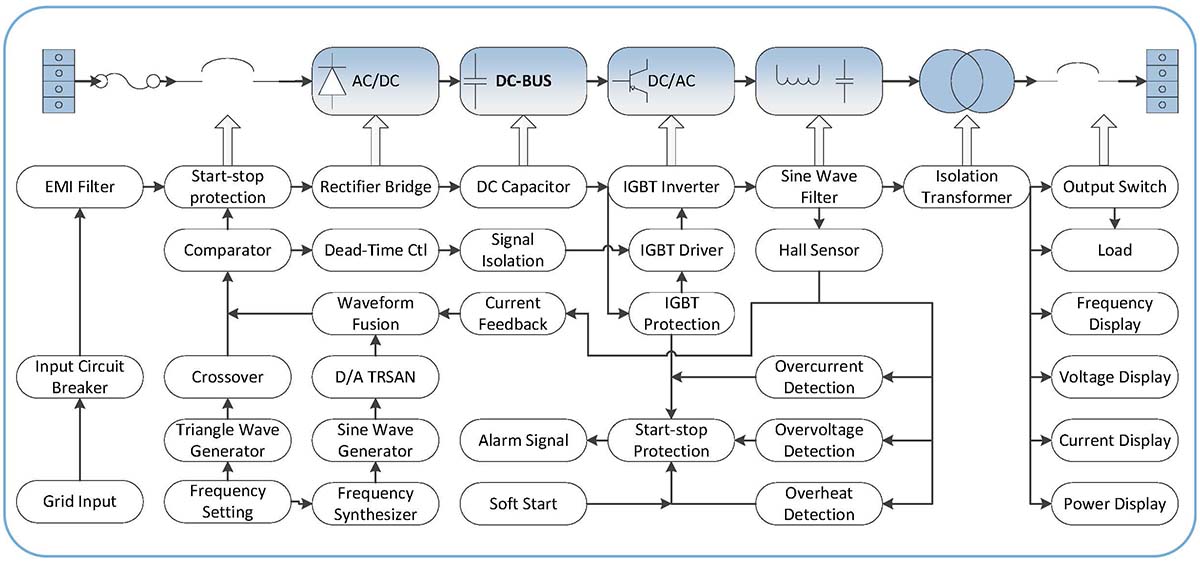
Dynamic Voltage Restorer Control principle topology diagram
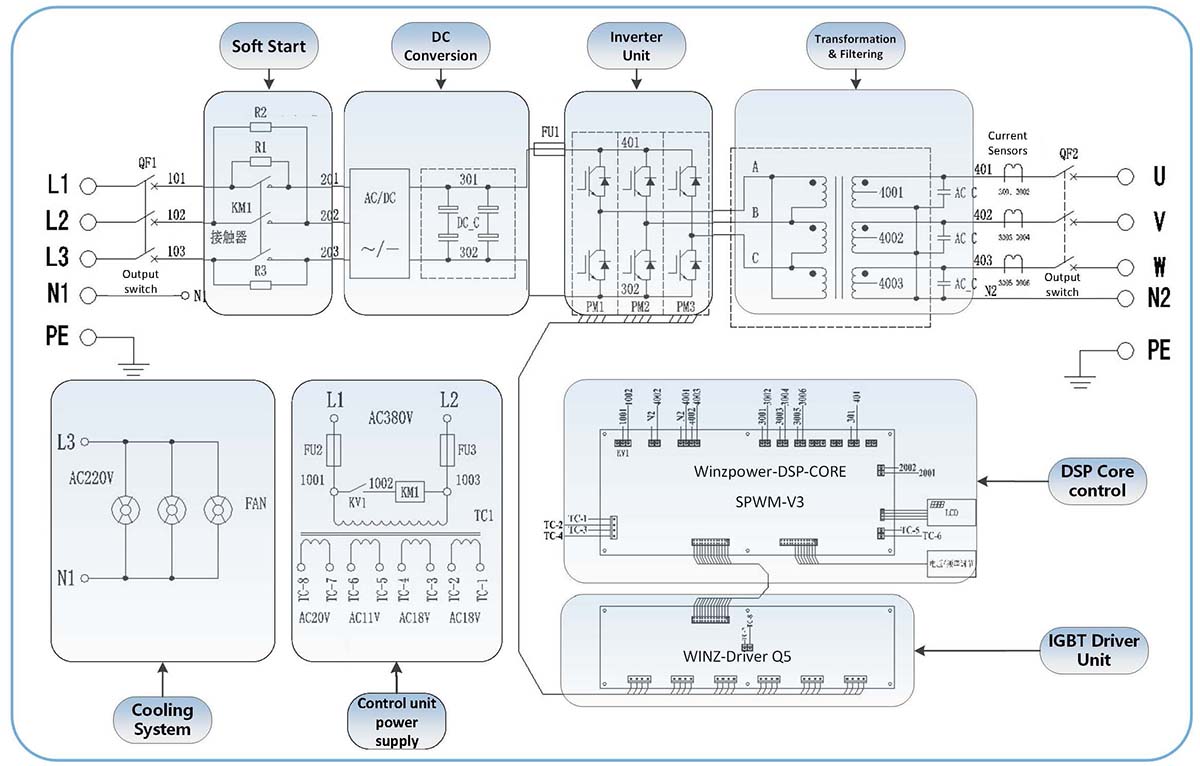
List Of DVR Technical Parameters
|
Voltage level |
208V 400V 690V 10KV |
|
Rated capacity |
50kVA-5000kVA |
|
Compensation range |
0%-130% |
|
Compensation time |
0.4-30s (time can be customized) |
|
Continuous voltage sag protection |
CAN |
|
Working frequency |
50/60Hz±10% |
|
Efficiency |
99.2% |
|
Overload and short-circuit protection |
Breaker |
|
Overload capacity |
Thyristor overload 150%, maintain 60s, overload 500%, maintain 1s |
|
Three-phase grid type |
Three-phase three-wire / three-phase four-wire |
|
Compensation voltage settings |
CAN |
|
Compensation action threshold settings |
CAN |
|
Output frequency |
50/60Hz±10% |
|
Voltage compensation accuracy error |
<1% |
|
Voltage distortion ratio THDU |
On linear load condition <3% |
|
Voltage imbalance |
On 100% unbalanced load condition <3% |
|
Voltage compensation response time |
Less than 2ms |
|
Response time |
50us |
|
Load power factor |
0.5 lag to 0.9 lead |
|
Energy storage component |
Super capacitor |
|
Working temperature |
-25~+45℃ |
|
Charge and discharge cycle number |
>1,000,000 times |
|
Designed life span |
15 years (25℃) |
|
Overload capacity |
200% |
|
Re-charge time |
<45s |
|
Measurement method |
Phase-voltage / line voltage |
|
Event resolution |
10ms |
|
Detection period |
50us |
|
Interface |
RS485、CAN |
|
Protocol |
Modbus |
|
HMI |
8 inch or above touch screen |
|
Failsafe bypass |
Bypass contactor |
|
Maintenance bypass |
Bypass breaker |
|
Cooling |
Forced air cooling |
|
Noise(dB) |
<40 |
|
Working temperature |
-25~45℃(above 45℃, derating 2% for every 1℃rising) |
|
Operation humidity |
0-95% no gel |
|
Working altitude |
0-3000m(>2000m, derating 1% for every 100m rising) |
|
Protection class |
IP21 or IP23, other class can be optional |
List of DVR Power Models & Products
1.Three-phase Model List
|
Model |
Capacity |
Dimension |
Voltage Grade |
|
DVR-100-0.4-N-3P |
100KVA |
800*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-150-0.4-N-3P |
150KVA |
800*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-200-0.4-N-3P |
200KVA |
1500*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-300-0.4-N-3P |
300KVA |
1500*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-400-0.4-N-3P |
400KVA |
2500*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-500-0.4-N-3P |
500KVA |
3000*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-600-0.4-N-3P |
600KVA |
3000*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-750-0.4-N-3P |
750KVA |
4000*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-900-0.4-N-3P |
900KVA |
4000*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-1000-0.4-N-3P |
1000KVA |
5200*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
|
DVR-1200-0.4-N-3P |
1200KVA |
5200*1000*2200 |
0.4KV |
What is voltage sag?
Voltage sag, also known as voltage drop, voltage sag, and voltage oscillation, is a type of voltage sag. It refers to the phenomenon where the effective value of voltage suddenly drops and then suddenly returns to normal.
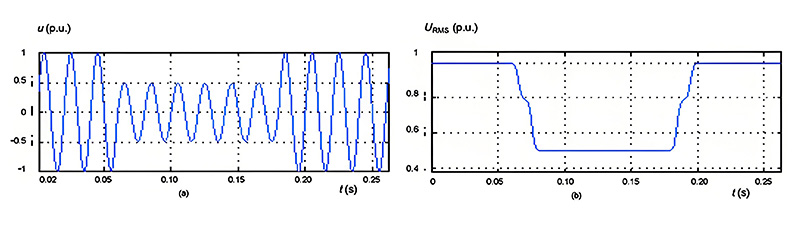
What is the cause of voltage sag?
There are many reasons that can cause voltage sag, such as short circuit faults, lightning strikes, and large motor startups in power transmission and distribution systems. Therefore, voltage dips cannot be avoided.
| Weather reasons | Occasional events | Other faults |
| As most transmission lines are exposed to nature, they are easy to break down the insulation medium between lines due to the impact of lightning, rainstorm and strong wind, resulting in the discharge between lines or lines to ground and voltage sag. | Traffic accidents, construction damage to transmission lines, human operational errors, and the entry of small animals into distribution rooms can also cause discharge between lines or to ground, resulting in voltage sag. | The starting of large motors, short circuit faults, line switching, and distribution equipment failures can also cause voltage sag. |
 |
 |
 |
What are the hazards of voltage sag?
Voltage sag can cause misoperation (tripping) of sensitive controllers, resulting in computer system failure, automatic device stoppage or misoperation, and frequency converter stoppage, etc; Causing the contactor to trip or the low-voltage protection to start, resulting in the motor, elevator, etc. coming to a halt; Causing the extinguishing of high-temperature light sources (iodine tungsten lamps) and resulting in the loss of lighting in public places.
Voltage sag can cause significant economic losses to many industries. Such as damage and waste of silicon wafers in semiconductor products, scrapping of automotive engine products, scrapping of display products, interruption or disorder of assembly lines, and so on.
Voltage sag not only causes economic losses, but may also result in casualties and major safety production accidents. For example, computer-controlled neurosurgery, cardiovascular surgery, ophthalmic surgery, etc. in hospitals can have serious consequences when equipment cannot function properly due to voltage drops; In the petrochemical industry, temporary voltage drops can cause control system malfunctions, leading to the risk of short-term loss of control of pressure and flow
Cases and Gallery
DVR 3phase-250KVA(3S input 380V50Hz Output 380V50Hz)


SBW Servo Motor Voltage Stabilizer

Three-phase Dry-type Isolation Transformer

SVC Servo Motor Voltage Stabilizer

Three Phase Split-phase Automatic Voltage Stabilizer
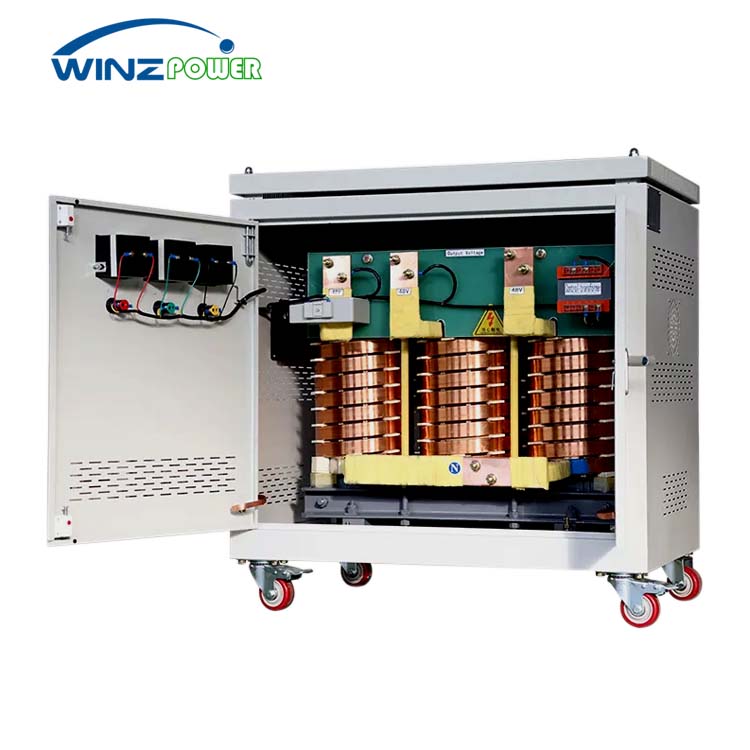

High-Current Dry Transformers
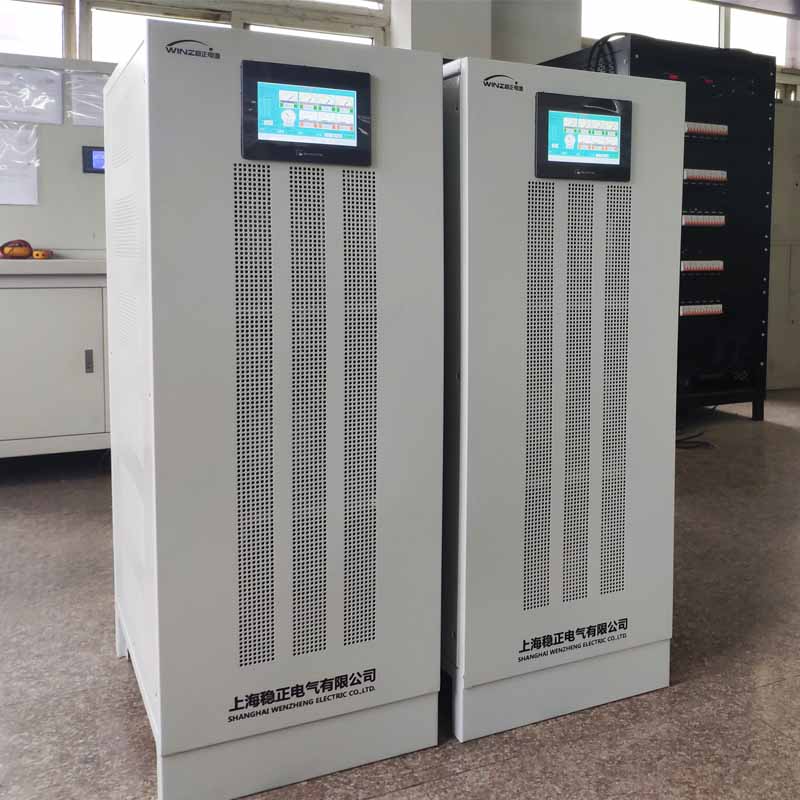

Static Non-contact SCR Voltage Regulator
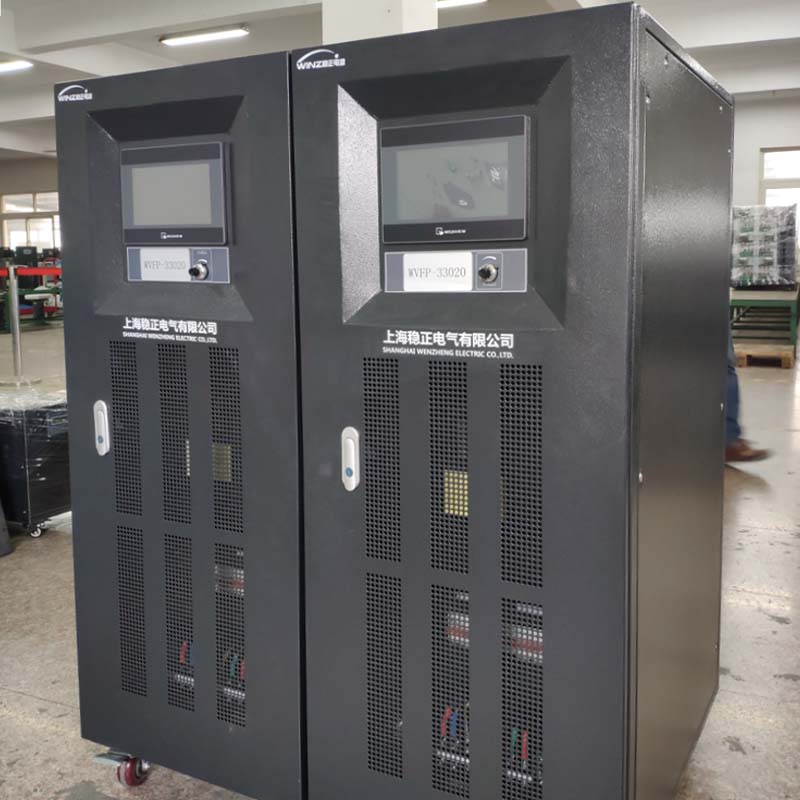

AC Variable Frequency Power Supply
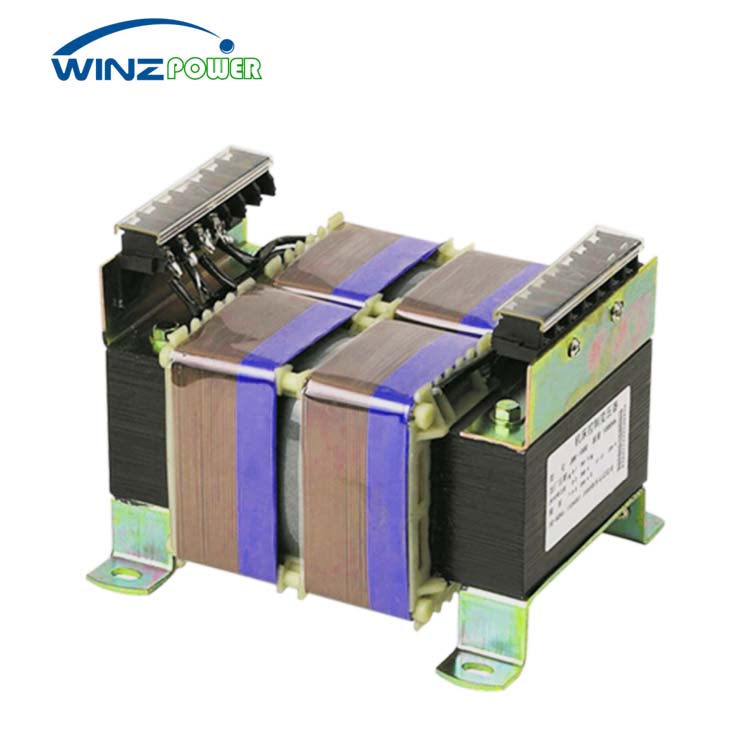

Low voltage control transformer






